Back to top
ChIP Sequencing

Investigate transcriptional regulation and active chromatin regions
ChIP sequencing allows for the genome-wide identification of transcription factor binding sites, histone modifications, and chromatin states. It helps you understand how gene regulation is altered across different biological conditions.
What You Can Achieve
- Detect genome-wide transcription factor binding sites
- Identify the impact of histone modifications on chromatin structure
- Explore regulatory changes under various experimental conditions
Before You Start
To ensure optimal experimental design, consider the following questions:
- Is a suitable reference genome available for alignment?
- Are you targeting narrow peaks (e.g., transcription factors) or broad peaks (e.g., histone modifications)?
- What sequencing depth is appropriate for your biological question?
- Have you defined replicates, controls (e.g., input DNA), and experimental conditions?
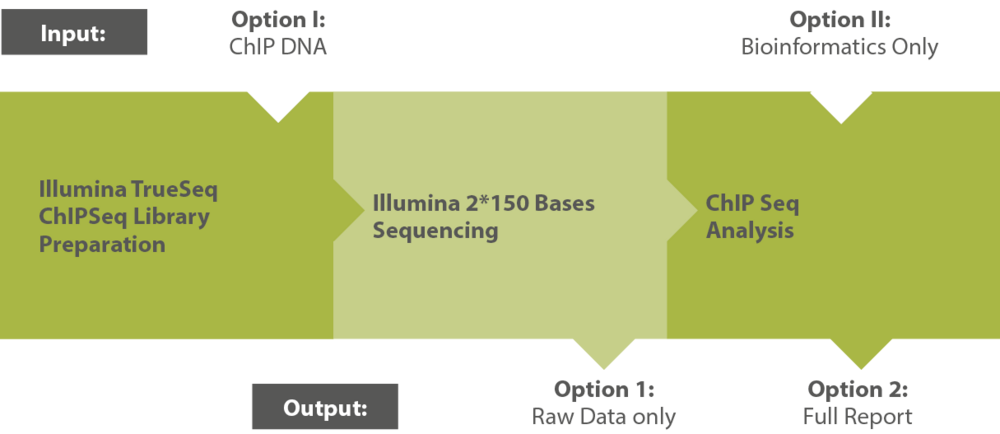
Modular Workflow
Outsource the entire workflow—or select specific modules. Our process is designed for flexibility. Typical workflow steps include:
Bioinformatic Analysis
Our standard bioinformatics package includes:
- Peak detection: Identification of enriched binding regions across the genome
- Motif analysis: Discovery of known and novel DNA-binding motifs
- Pathway analysis: Insight into potentially affected cellular pathways
Results are provided in both raw and analyzed formats—ready for downstream interpretation or publication.
Turnaround Time
- 25 working days from sample receipt for library preparation and sequencing
- +10 working days for data analysis
- Express service available upon request
Sample Requirements
- Buffer recommendation: 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5–8.5)
- Important: Avoid any buffers containing EDTA >1mM
- DNA quantification: Use fluorometric methods (e.g., PicoGreen®, Qubit®)
Sample Amounts for Illumina Sequencing:
| Type of Library | Amount (µg) | Concentration (ng/µl) |
| ChIP-Seq libraries | >0.05 | >5 |