Back to top
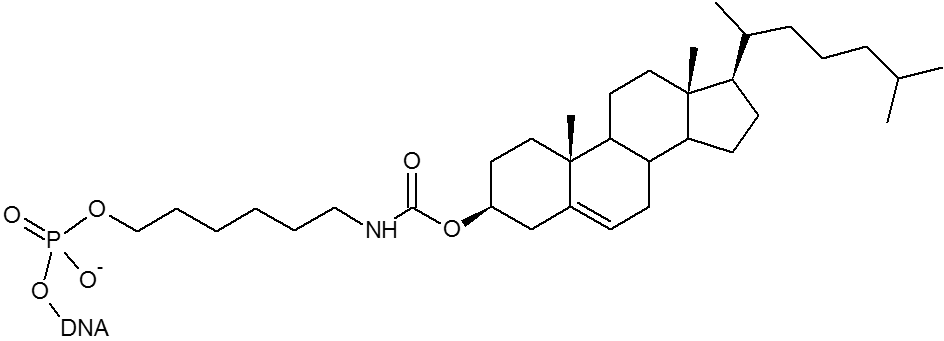
Cholesterol is used to improve cellular uptake. By conjugating oligonucleotides to the non-toxic and hydrophobic cholesterol the oligonucleotide permeates better through the cell membrane.
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| 3' |
X
|
X
|
O |
X
|
X | ||
N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc)
Conjugation of N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) has become a major clinical strategy for delivery of oligonucleotides to hepatocytes (liver cells). Such conjugates are efficiently internalized by binding to the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGR), which exhibits high affinity for N-acetyl galactosamine terminated oligosaccharides.
Various GalNAc cluster types available
Please contact us to discuss the best option for your application
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
HPLC & Dialysis |
| 3' |
X
|
X
|
O |
X
|
X | ||
| 5' |
O
|
O
|
O |
X
|
X | ||
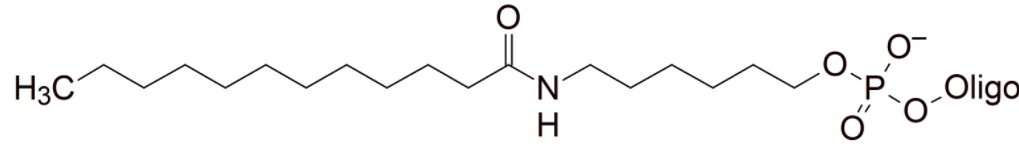
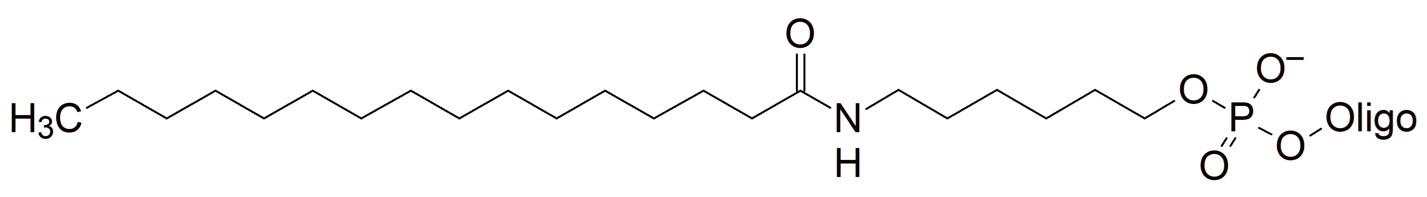
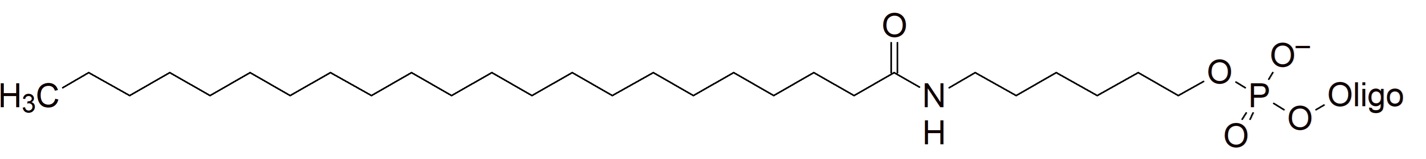
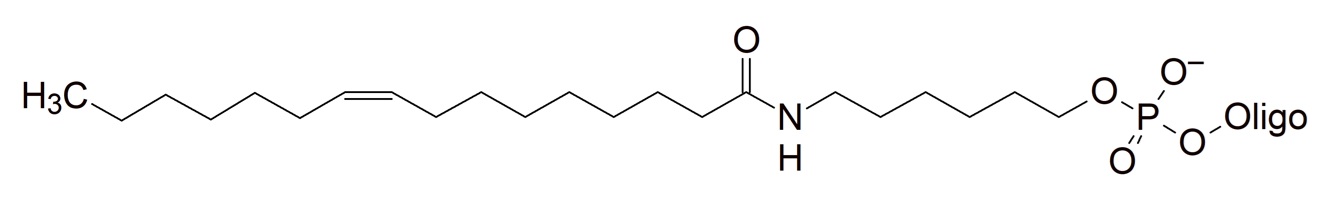
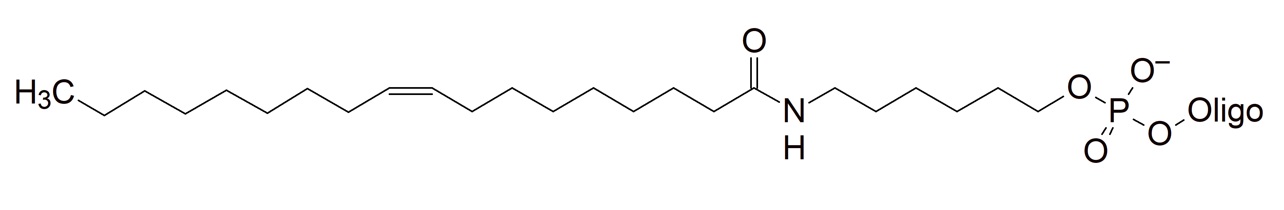
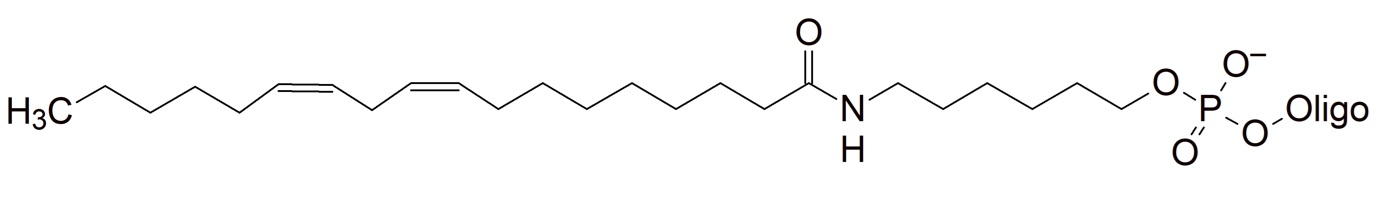
Lipids
These modifications introduce a highly hydrophobic residue into the oligonucleotide. They are currently under investigation for oligonucleotide conjugations that could potentially help improve cell delivery and potentially increase the half-life of therapeutic oligonucleotides (ASO) in vivo.
| Modification | Position | Synthesis Scale [µmol] | Purification | |||||
| 0.04 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 15 | Des | HPLC | HPLC & Dialysis | ||
| Palmitate (Palmitic acid (C16)) | 5' | O | O | O | X | X | ||
| Palmitate (Palmitic acid (C16)) | 3' | O | O | O | X | X | ||
|
Lauric acid (C12) Behenic acid (C22) Palmitoleic acid (C16:1) Oleic acid (C18:1) Linoleic acid (C18:2) Eicosapentaenoic acid (C20:5) |
3' or 5' | O | O | O | O | O | ||
|
Other lipids |
Please send us a request specifying your desired lipid, and we'll gladly explore how we can assist you.
|
|||||||