
Back to top
Antisense Oligos

- 2'-O-Methyl
- 2'-Fluoro
- MOE (2'-methoxyethyl)
- LNA (locked nucleic acid)
- S-cEt (constrained ethyl, on request)
- PTO (phosphorothioate)
- Gapmers
- GalNAc
Features and Benefits
- Alle ASOs werden vor dem Versand mit MALDI-TOF MS kontrolliert
- Renommierter ASO-Lieferant für Top-Forschungsinstitute und Pharma/Biotech-Unternehmen
- Oligonukleotide mit niedrigem Endotoxingehalt (<0.5 EU/mg), bitte fordern Sie ein Angebot an
- Synthesemaßstäbe bis 15 µmol werden innerhalb von 4 bis 6 Tagen verschickt
- Für In-vivo-Anwendungen beträgt die Produktionszeit ab 3 Wochen, einschließlich Endotoxintests
- Ausgebildete und erfahrene Wissenschaftler unterstützen Sie gerne
- Wettbewerbsfähige Preise
- Hohe garantierte Ausbeuten
- Analytische HPLC verfügbar
- Analysenzertifikat verfügbar
- Einfach zu bedienendes Online-Portal mit einer Reihe von hilfreichen Tools (z.B. Auftragsverfolgung & Historie, komfortable Suche und Nachbestellmöglichkeit)
Übersicht
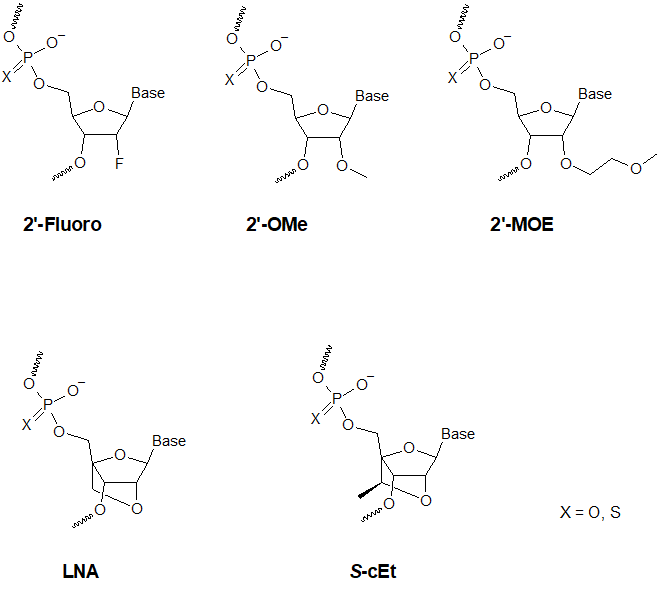
-
PTO (phosphorothioates) modifications: PTOs contain one sulfur atom in place of an oxygen atom in the internucleotide linkage of DNA or RNA. This modification of the normal phosphodiester backbone is characterized by an increased cell uptake, high nuclease resistance and elicitation of RNAse H activity.
- 2'-O-Me-RNA modifications: The incorporation of 2'-O-Methyl RNA nucleotides induces a resistance to a wide variety of nucleases, in particular RNase. Furthermore, 2’-OMe oligonucleotides show slightly increased affinity towards their complementary mRNA target sequence, thereby forming more stable hybrid duplexes compared to their non-modified DNA or RNA counterparts. This enables the formation of more stable hybrids with complementary RNA strands than would be the case for non-modified DNA and RNA sequences.
-
2'-MOE-RNA modifications: Oligonucleotides incorporating 2'-O-methoxyethyl (MOE)-modified nucleotides, can support most, if not all antisense mechanisms of action. Further key distinctive characteristics are nuclease resistance, lower toxicity, superior target binding specificity, as well as increased affinity towards complementary RNA. For more detailed information about 2'-MOE antisense oligonucleotides from Microsynth, please see the flyer on the right side.
-
LNA modifications: LNA containing oligonucleotides offer substantially increased affinity for its complementary strand, compared to traditional DNA or RNA oligonucleotides. This and the concomitant high nuclease resistance of LNAs results in unprecedented sensitivity and specificity and makes LNA™ oligonucleotides ideal for use in antisense applications.
- S-cEt modifications: cEt oligonucleotides (constrained ethyl nucleotides) are an advancement of LNA oligonucleotides. They have been developed for antisense applications and are mainly used in gapmers. Such ASOs show superior stability towards nuclease degradation compared to LNA without compromising binding selectivity or hybridization stability.
- N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc): Conjugation of N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) has become a major clinical strategy for delivery of oligonucleotides to hepatocytes (liver cells). Such conjugates are efficiently internalized by binding to the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ASGR), which exhibits high affinity for N-acetyl galactosamine terminated oligosaccharides.
To learn more about specifications of these five types of modifications, please see the table below.
Key Specifications:
|
Modifications |
Position |
Synthesis scale [µmol] | Purification1 | |||||
|
5’ |
3’ |
Int. |
0.04 |
0.2 |
1 |
15 |
HPLC + Dialysis |
|
|
PTO |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
||
| 2’-O-Me-RNA |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
x |
| 2'-MOE-RNA | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| LNA | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | x |
| GalNAc | x | x | x | x | x | |||
1 We strongly recommend to order ASOs with “HPLC + Dialysis” purification. The Na+ salt exchange is necessary to remove toxic salts from HPLC purification. For in vivo testing we recommend our low endotoxin oligonucleotides.
Synthese Massstäbe
Nur 2' OMe, 2' MOE in Kombination mit oder ohne PTO
Desalted
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 3 | 15 | 2-3 |
| 0.2 µmol | 10 | 50 | 2-3 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 30 | 150 | 2-3 | |
| 15 µmol | 600 | 3'000 | 3-5 | |
HPLC
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 1 | 5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 3 | 15 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 10 | 50 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | 300 | 1'500 | 4-6 | |
HPLC & Dialysis
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | - | - | - |
| 0.2 µmol | 3 | 15 | 3-5 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 10 | 50 | 3-5 | |
| 15 µmol | 250 | 1'250 | 5-7 | |
PAGE
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 2 | 10 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 7 | 35 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | - | - | - | |
Gapmere (einschliesslich DNA und 2' OMe oder 2' MOE)
HPLC
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 1 | 5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 3 | 15 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 8 | 40 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | 300 | 1'500 | 4-6 | |
HPLC & Dialysis
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | - | - | - |
| 0.2 µmol | 3 | 15 | 3-5 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 8 | 40 | 3-5 | |
| 15 µmol | 250 | 1'250 | 5-7 | |
PAGE
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 2 | 10 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 7 | 35 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | - | - | - | |
Gapmere (einschliesslich DNA und LNA)
HPLC
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 1 | 5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 2 | 10 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 6 | 30 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | 250 | 1'250 | 4-6 | |
HPLC & Dialysis
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | - | - | - |
| 0.2 µmol | 2 | 10 | 3-5 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 6 | 30 | 3-5 | |
| 15 µmol | 200 | 1'000 | 5-7 | |
PAGE
| Synthesis scale1 | Length Restriction | Guaranteed Yield2 | Production Time [wd] | |
| [OD260] | [nmol]3 | |||
| 0.04 µmol | 13 - 30 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 3-4 |
| 0.2 µmol | 2 | 10 | 3-4 | |
| 1.0 µmol | 5 | 25 | 3-4 | |
| 15 µmol | - | - | - | |
1 Die Syntheseskala stellt die Ausgangsmenge an 3'-Basen (Ausgangsmaterial) dar.
2 Unsere garantierten Ausbeuten sind in OD gemessen.
3 Die in nmol angegebenen Ausbeuten stellen eine Beispielrechnung für ein 20mer dar. Für diese Berechnung wurde die folgende Faustformel angewendet: nmol Oligo = OD x 100/Länge des Oligos. Bitte beachten Sie, dass diese Berechnung auf Sequenzen mit nahezu homogener Verteilung der 4 DNA-Basen basiert; sie kann bei Sequenzen mit hohem GC-Gehalt >70% etc. abweichen.
Wie bestellen
- Besuchen Sie unseren Webshop
- Klicken Sie auf DNA im blauen Bereich "DNA/RNA-Synthese".
- Wählen Sie entweder "Normal Entry", um die gewünschten Sequenzinformationen etc. einzutippen oder zu kopieren/einzufügen, oder wählen Sie alternativ "Upload Entry", indem Sie unsere praktische Excel-Vorlage verwenden (kann in unserem Webshop heruntergeladen werden).
- Geben Sie 5,6,7,8 für jede einzelne zu ersetzende Base innerhalb der Sequenz ein
- Definieren Sie die innere Modifikation (5=...), indem Sie die gewünschte Modifikation aus dem Dropdown-Menü auswählen (z. B. 5=...2'-O-Methyl-RNA-A, 6=...2'-O-Methyl-RNA-C usw.)
- Geben Sie 5,6,7,8 für jede einzelne zu ersetzende Base innerhalb der Sequenz ein
- Definieren Sie die innere Modifikation (5=...), indem Sie die gewünschte Modifikation aus dem Dropdown-Menü auswählen (z. B. 5=...2'-Methoxyethyl-ribo-A, 6=...2'-Methoxyethyl-ribo-mC usw.)
- Geben Sie 5,6,7,8 für jede einzelne zu ersetzende Base innerhalb der Sequenz ein
- Definieren Sie die innere Modifikation (5=...), indem Sie die gewünschte Modifikation aus dem Dropdown-Menü auswählen (z. B. 5=...LNA-A, 6=...LNA-C usw.)
- cEt ASOs sind nur auf Anfrage erhältlich. Bestellhinweise folgen zusammen mit dem Angebot.
- Endotoxinarme ASOs sind nur auf Anfrage erhältlich. Bestellanweisungen folgen zusammen mit dem Angebot.

