Back to top
Functional Groups (für ASOs und siRNAs)
|
Functional Groups
|
Position
|
||
|
|
5’
|
3’
|
int
|
| Amino / Amino-dT |
X
|
X
|
X
|
| Phosphorothioate (PTO) |
|
|
X
|
| Mesyl |
|
|
X
|
| Phosphoryl guanidine (PN) |
|
|
X
|
Amino / Amino-dT
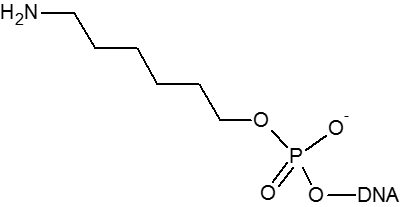
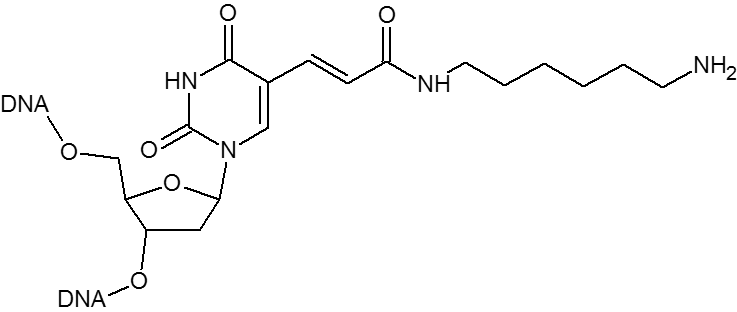
A primary amino group can be used to attach a variety of modifiers (such as fluorescent dyes) to an oligonucleotide or used to attach an oligonucleotide to a solid surface. Amino modifiers can be positioned at the 5’-end with either a standard (C6) or longer (C12) spacer arm. Amino modifications can be positioned at the 3’-end. Internal amino modifications can be introduced using an amino-dT base.
|
Functional Group
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
|
| Amino C6 |
5’
|
X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
|
3’
|
X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
|
Amino C6-dT
|
Int
|
|
X | X | O |
|
X | X |
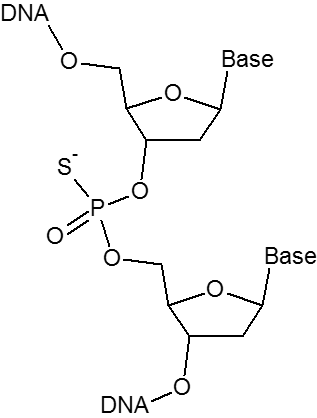
The phosphorothioate (PTO) bond substitutes a sulfur atom for a non-bridging oxygen in the phosphate backbone of an oligo. This modification renders the internucleotide linkage resistant to nuclease degradation. Phosphorothioate bonds can be introduced between the last 3-5 nucleotides at the 5'- or 3'-end of the oligo to inhibit exonuclease degradation. Including phosphorothioate bonds throughout the entire oligo will help reduce attack by endonucleases as well.
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| Int | X |
X
|
X
|
X | X |
X
|
X |
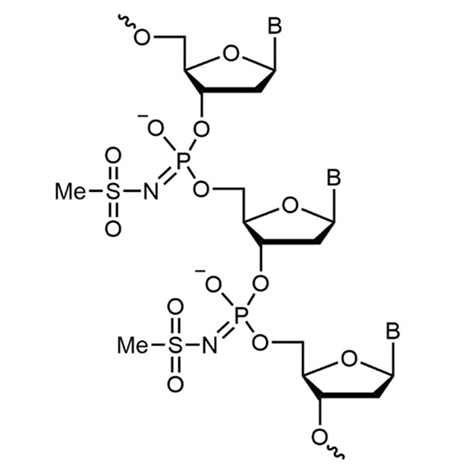
The mesyl (µ) modification introduces a mesyl phosphoramidate linkage in place of the normal phosphate bond. This backbone change protects oligos against degradation by both endo- and exonucleases, while maintaining RNA binding and RNase H activity. Replacement of phosphodiester or phosphorothioate bonds with mesyl bonds can improve the ASO activity through reduced immune stimulation, cytotoxicity and improved stability.
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| Int | X |
X
|
X
|
X | X |
X
|
X |
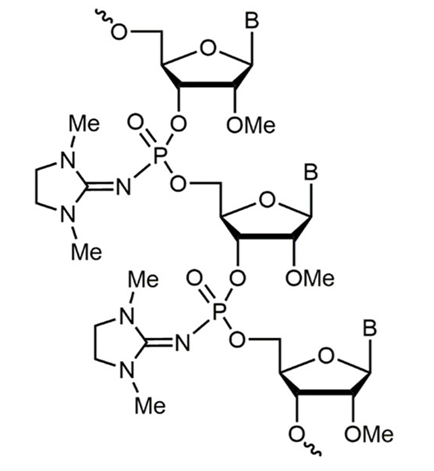
Phosphoryl guanidine (PN) bonds replace the normal phosphate linkage with a guanidine group. This modification greatly enhances resistance to nuclease degradation, while keeping oligos electrically neutral. PN bonds can improve stability and cellular uptake in biological samples and thereby result in increased activity of the ASO.
|
Position
|
Synthesis Scale [µmol]
|
Purification
|
|||||
|
|
0.04
|
0.2
|
1.0
|
15
|
Des
|
HPLC
|
PAGE
|
| Int | X |
X
|
X
|
X | X |
X
|
X |